NTC thermistors are crucial in temperature sensing and measurement in various industries and applications. These specialized temperature sensors offer unique advantages that make them highly sought after in electronic devices, automotive systems, medical equipment, and much more.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of NTC thermistors, exploring their working principles, types, advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications.
Part 1. What is an NTC thermistor?
An NTC thermistor, or Negative Temperature Coefficient thermistor, is a specialized type of temperature sensor that exhibits a decrease in resistance as the temperature rises. It is a device made from semiconductor materials with the unique property of changing their electrical resistance in response to changes in temperature. The “negative temperature coefficient” refers to the inverse relationship between the resistance and temperature of the thermistor.
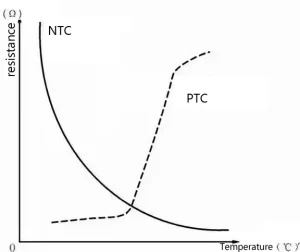
Part 2. How do NTC thermistors work?
The working principle of NTC thermistors is based on the behavior of semiconductor materials. These thermistors use metal oxides, ceramics, or polymers with a negative temperature coefficient. As the temperature increases, the movement of charge carriers within the material also increases, resulting in a decrease in resistance.
The resistance-temperature relationship of an NTC thermistor is highly nonlinear. This nonlinearity allows for precise temperature sensing within a specific temperature range. NTC thermistors are characterized by their resistance at a reference temperature, known as the “nominal resistance,” and their resistance-temperature curve, or “R-T curve.”
Part 3. NTC thermistor types

Bead Type NTC Thermistors
These are the most common NTC thermistors, consisting of a minor, bead-like component typically made of a ceramic material with added metallic oxides. They are compact, durable, and offer precise temperature measurements.
- Application: Bead-type NTC thermistors are widely used in temperature sensors for electronic devices, battery packs, medical equipment, and home appliances.
Chip Type NTC Thermistors
Chip NTC thermistors are designed for surface mounting on circuit boards. They come in a flat, rectangular shape, making them suitable for limited-space applications. Chip thermistors are widely used in electronics and automotive industries.
- Application: Chip NTC thermistors are commonly used for temperature compensation in integrated circuits, battery management systems, temperature-controlled switches, and automotive engine control units.
Glass Encapsulated NTC Thermistors
These thermistors are encapsulated within a glass shell, providing excellent stability and protection against environmental factors such as moisture and chemical exposure. They are commonly used in harsh environments or applications requiring high reliability.
- Application: Glass-encapsulated NTC thermistors find applications in temperature measurement and control in industrial processes, automotive under-the-hood sensing, HVAC systems, and medical devices.
Probe Type NTC Thermistors
Probe thermistors feature a cylindrical or rod-shaped design with a metal housing at one end and the sensing element at the other. They are ideal for temperature sensing in liquids, gases, or surfaces requiring direct contact.
- Application: Probe-type NTC thermistors are used in food processing equipment, HVAC systems, automotive coolant temperature sensing, environmental monitoring, and laboratory equipment.
Surface Mount NTC Thermistors
Surface mount thermistors are designed for automated assembly onto circuit boards using reflow soldering techniques. They offer convenience in manufacturing processes and are commonly used in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
- Application: Surface mount NTC thermistors are used for temperature monitoring and control in battery chargers, power supplies, LED lighting, consumer electronics, and industrial automation systems.
Ring Lug Type NTC Thermistors
These thermistors feature a ring lug terminal for easy installation and connection. They are commonly used in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, automotive applications, and industrial equipment for temperature monitoring and control.
- Application: Ring lug-type NTC thermistors find applications in temperature sensing and control in water heaters, air conditioners, refrigerators, automotive air intake systems, and industrial machinery.
Part 4. NTC thermistor advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- High Sensitivity: NTC thermistors exhibit high sensitivity to temperature changes, making them ideal for precise temperature measurement and control in various applications.
- Wide Temperature Range: They operate across a wide temperature range, from cryogenic temperatures to several hundred degrees Celsius, allowing versatility in different environments.
- Fast Response Time: NTC thermistors respond rapidly to temperature changes, enabling quick and accurate temperature sensing and control in dynamic systems.
- Compact Size: NTC thermistors are available in small, compact sizes, making them suitable for integration into space-constrained electronic devices and systems.
Disadvantages:
- Nonlinear Response: One of the main drawbacks of NTC thermistors is their nonlinear temperature-resistance characteristics, requiring linearization techniques for precise temperature measurement.
- Limited Operating Range: While NTC thermistors cover a wide temperature range, they may not be suitable for extreme conditions outside their specified operating range.
- Self-Heating Effect: NTC thermistors exhibit a self-heating effect when a current passes through them, leading to inaccuracies in temperature measurement, especially at higher currents.
Part 5. Why do lithium batteries need NTC thermistors?
Overheat Protection: NTC thermistors help detect and prevent overheating during charging or discharging cycles, reducing the risk of thermal runaway.
Temperature Monitoring: They continuously monitor battery temperature, allowing for temperature-dependent charging/discharging algorithms to optimize performance.
Cell Balancing: NTC thermistors ensure uniform temperature distribution among cells in multi-cell battery packs, preventing hot spots.
Early Warning System: They warn about potential battery faults or malfunctions, enhancing safety.
Thermal Management: NTC thermistors aid in adjusting cooling mechanisms to maintain batteries within safe operating temperatures, thus preventing degradation.
Part 6. FAQs
-
What is the difference between NTC and PTC thermistors?
NTC thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient, meaning their resistance decreases as temperature increases. PTC thermistors have a positive temperature coefficient, with resistance increasing as temperature rises. -
Why is NTC thermistor used over PTC?
NTC thermistors are often preferred for temperature sensing and control because they exhibit a more linear response over a more comprehensive temperature range. They are also more sensitive to temperature changes and offer excellent stability in circuit applications. -
Why is NTC used in circuits?
NTC thermistors are used in circuits for temperature sensing, compensation, and control. They provide accurate and reliable temperature measurements, allowing circuits to adjust parameters based on temperature changes to ensure optimal performance and safety. -
How do I choose a NTC thermistor?
When choosing an NTC thermistor, consider the desired temperature range, accuracy requirements, response time, and physical size constraints. Additionally, ensure compatibility with the circuit and application requirements. -
What is the difference between a thermocouple and an NTC thermistor?
Thermocouples generate a voltage proportional to the temperature difference between two points. At the same time, NTC thermistors change resistance in response to temperature variations. Thermocouples are typically used for high-temperature measurements. NTC thermistors are more suitable for lower temperature ranges and offer simpler interfacing with electronic circuits.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Overview of Deep Cycle Lithium Battery
In this article, we explore the life, voltage, capacity, and charging considerations of deep cycle lithium batteries.
How Long do Lithium Batteries Last?
How long do lithium batteries last? we will explore the factors that influence the lifespan of lithium batteries and provide insights into their longevity.
How to Choose the Best LiFePO4 Battery?
Choose LiFePO4 batteries for superior performance, safety, and versatility in EVs, UPS, and backup power. This guide helps you make informed decisions.
Get 12v Lithium Car Battery As a Power Source for the Ride
Make the right choice for your vehicle's battery needs by installing a 12 volt lithium car battery. You will enjoy maintenance-free longevity with this change.
Everything About A Small Lithium Ion Battery
Discover the features, uses & future potential of a small lithium ion battery. A compact and tiny powerhouse ideal for smartphones, wearables, drones & more.





